The Republic of Seychelles is an archipelago of islands in the Indian Ocean, off East Africa. It has a relatively small population of around 100K people at the time of writing.
It stands out among its fellow African countries in terms of its progress on the education front. It is also one of the most developed nations in Africa and has the highest GDP per capita in the continent by late 2022. After becoming a high-income country in the World Bank’s books in 2014, it has been the only high-income country in Africa, closely followed by Mauritius.
In this article, we will be taking a look at the specifics of education statistics in Seychelles and some of the reasons behind their success.
Key Education Statistics in Seychelles
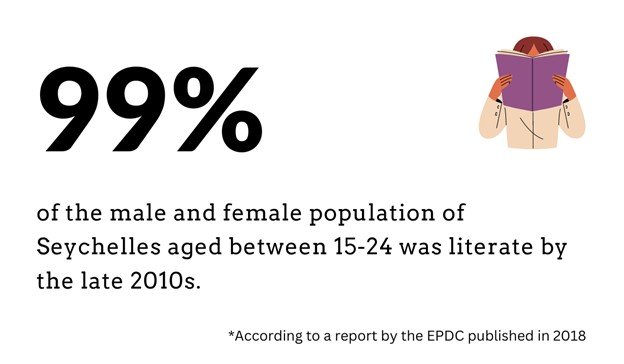
- According to a 2018 report by the EPDC, 99% of the male and female population aged 15-24 in Seychelles were literate. This is at par with international standards.
- Similarly, 94% of the male and 93% of the female population aged 15 and above in Seychelles were literate. This is a little lower than the international standard.
- According to the same source:
- On the primary level, the GER for males and females was 113% and 112%, respectively.
- On the lower secondary level, the GER for males and females was 126% and 124%, respectively.
- On the higher secondary level, the GER for males and females was 63% and 75%, respectively.
- Around 6% of children in Seychelles were out of school by 2009. According to the World Bank, this decreased to about 1.4% by 2018.
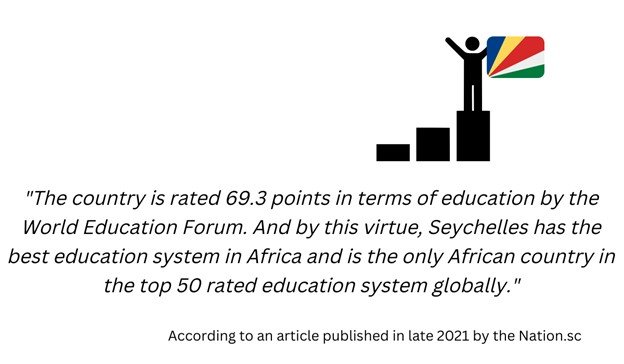
- According to metrics by the World Education Forum, Seychelles was the only African nation in the global top 50 education systems by 2021.
What is the Literacy Rate in Seychelles?
According to data from the World Bank, cited by Macrotrends, the adult literacy rate in Seychelles for people aged 15 and above is as follows.
The latest data collected in this regard was in 2018. Till then, Seychelles’ literacy rate was 95.87%. This shows a nominal increase of 1.91% in the country’s literacy rate since 2010. Including the most recent 2018 data, the previously recorded literacy rates of the country are as follows:
- 2018 – 95.87%
- 2010 – 93.95%
- 2000 – 91.84%
- 1994 – 87.81%
According to Study Country, Seychelles had already reached a 90% literacy rate around the late 1980s. Since then, the rate has continued to go up steadily. However, the change has been insignificant because of the little room left to improve.
Similarly, a report by the Education Policy Data Center published in 2018 shows how Seychelles was doing in youth literacy compared to other upper-middle-income countries. EPDC provides global education data, data visualization tools, and policy-oriented analysis to improve schools and learning in developing countries.
Notable statistics from the report include the following:
Youth – Age 15-24
99% of the male and female population of Seychelles was literate.
This is at par with other upper-middle-income countries.
Adults – Age 15+
93% and 94% of Seychelles’ male and female population was literate under this category.
This is lower than the 97% and 94% literacy rates of males and females in upper-middle-income countries.
How Does the Seychelles Education System Work?
We will briefly go through the structure of Seychelles’ education system according to information from the AACRAO Electronic Database for Global Education (EDGE) and the Education Policy and Data Center.
AACRAO EDGE has been one of the leading resources in the USA for evaluating educational credentials for countries across the globe for more than 15 years.
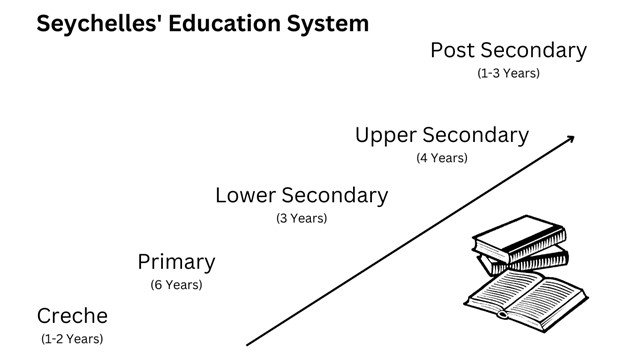
The Seychelles education system can be divided into the following five parts:
-
Pre-Primary
Children from ages 3 to 5 years old are admitted into institutes known as creches. These institutes allow children to learn things like:
- Reading
- Basic math
- Social skills
- Moral lessons
According to Study Country, around 90% of children aged four years attend these nurseries in anticipation of admission into primary schools.
-
Primary
According to the EPDC’s report mentioned above, the official age of entry for children joining primary schools is six years. Students transition towards six years of primary education after preschool.
-
Lower Secondary
The first half of secondary education lasts three years.
-
Upper Secondary
The second half of secondary education lasts four years. This may include education at the Seychelles Polytechnic and the National Institute of Education.
-
Post Secondary
According to the Webometrics Ranking of World Universities, the higher education institutes in Seychelles include the following:
- University of Seychelles
- University of Seychelles American Institute of Medicine and
- Seychelles Polytechnic Institute
Students that complete their secondary education can pursue further studies in these institutes.
How Many Children Go to School in Seychelles?
Children’s education in Seychelles begins in preschool nurseries or creches. We mentioned some of the things that preschoolers (children aged 3-5 years) learn in these institutions. It is also worth reiterating that 90% of the country’s preschoolers join nurseries in anticipation of joining primary schools.
The EPDC report mentioned above used data from different sources, including the World Bank and the UNESCO Institute of Statistics.
According to the report, a total of 5% of children were out of school by 2009. This included 6% of the female and 8% of the total relevant male population.
This number seems to have declined in the following decade. According to data from the World Bank, only about 1.4% of children were out of school in Seychelles by 2020.
The report also laid out data about the country’s Gross Enrollment Rates (GERs) and Net Enrollment Rates (NERs) for Primary, Lower Secondary and Upper Secondary education.
For reference purposes, according to UNESCO, a GER exceeding 100% indicates that a country can support all school-age children. This is because a GER considers all children regardless of age. As a result, underage and overage children are included as well as students of age.
An NER only takes students of age into account. The maximum here is 100%. According to the UN, the lower a country’s NER is from 100%, the more the percentage of children who are not enrolled.
The report’s findings are as follows:
1. Primary
Males
The GER for males was 113%, while the NER was 96%. This shows a difference between the overall children being enrolled and the children who are of the official age to join primary schools. The completion rate was 129%, while transitions to secondary education were 96%.
Females
The metrics of females in primary education were similar to that of males. The GER and NER were at 112% and 95%, respectively. The completion rate was 124%, and the transition to secondary education was 100%.
2. Lower Secondary
The GER for males and females was 126% and 124%, respectively.
3. Upper Secondary
The GER for this category is the lowest at 63% for males and 75% for females. This may indicate that a significant proportion of students in Seychelles may not be transitioning from lower secondary to upper secondary education.
The State of Female Education in Seychelles
As mentioned above, the literacy rate for females between the ages of 15 and 24 in Seychelles is 99%. However, the literacy rate for females above 15 years (with no upper limit) is 94%. Neither of these statistics indicates that females are suffering in Seychelles’ education system. Rather, they indicate that Seychelles is up to international standards for countries like itself and doing significantly better than its African neighbors.
Why is Seychelles’ Education System So Successful?
According to metrics by the World Education Forum, Seychelles had the best education system in the whole of Africa by 2021. It is the only African nation in the global top 50 education systems. The following are some of the reasons why the island nation is doing as well as it on the academic front.
-
Free Education
According to the Seychelles News Agency, the Seychelles education is free for students up to 18 years of age. This policy was implemented in 1978 and has carried on since then. It has helped earn Seychelles’ education system recognition across the globe.
-
Mandatory Education
According to the same source, education is compulsory for children as old as 16 years. This makes passing lower secondary education the mandatory threshold of academic qualification in the country.
-
Relatively Small Population
Having a smaller population helps Seychelles implement policies and impose educational regulations. According to the Worldometer, Seychelles is ranked 200 out of 225 countries in terms of population.
-
A Strong Economy
According to the World Bank, at $13,306, Seychelles had Africa’s highest GDP per capita in 2021. This allows the country to allocate the resources necessary to make education free and provide children with quality learning opportunities.
According to an article published by the Nation in August 2021, one of the country’s news agencies, Seychelles spends between 9-19% of its budget on education.
Conclusion
The literacy rate in Seychelles is around 99% for adults. The GERs for both primary and lower secondary education are above 100%, indicating an abundance of resources for the country’s educational needs. However, upper secondary education has noticeably low GERs for both genders. This may be because of the exclusion of students who enroll in vocational institutions.
Only a nominal percentage of children in Seychelles are out of school. In fact, a majority of kids below the official primary school-going age join pre-primary education in creches.
Seychelles’ free and mandatory education policies have been hailed worldwide and exhibit stellar results. They help make the country Africa’s North Star when it comes to setting the standards of education. However, it is also worth mentioning that the country enjoys the highest per capita income in the continent. This gives it a lot more resources to spare for education than its far less equipped African neighbors.







![Education and Skills Gap Statistics in the US [3 FAQs] 14 Education and Skills Gap Statistics in the US](https://zoets.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/pexels-kai-pilger-414530-scaled-e1704203026801.jpg)