Youth employment can benefit a country’s economy because it contributes to the rise in labor participation. It can engrave a work ethic within the youth at an early age and develop valuable skills.
The European Union (EU) is a union based on shared political and economic gain for members of the alliance. They published a report known as The European Union: What It Is and What It Does, which stated that there are 27 European countries, and the benefits these countries offer extend to European countries and abroad. The association joined forces to foster economic cooperation and encourage trade.
Youth employment is a crucial indicator of how a country’s economy is doing. So let us explore youth employment in the European Union.
Youth Employment Statistics in EU Member States
Key Facts
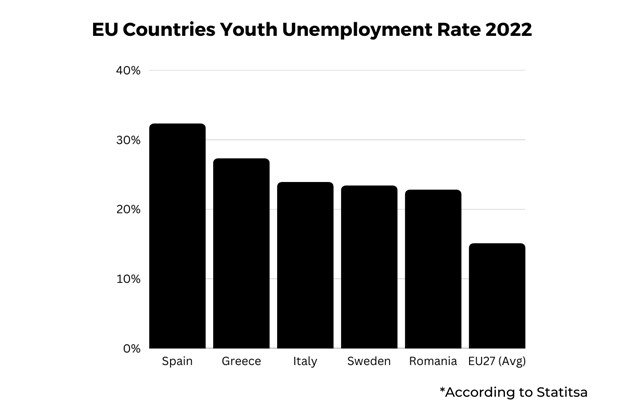
- According to Statista, Spain had the highest unemployment rate among EU member countries, in 2022, at 32.3%.
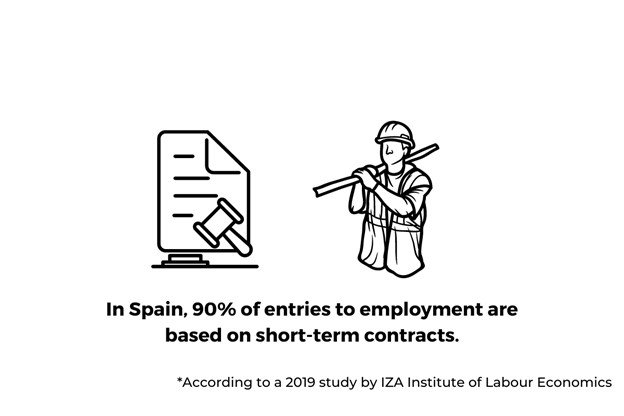
- According to the IZA Institute of Labor Economics, Spain’s entrance to the workforce consists of 90% of fixed and temporary contracts.
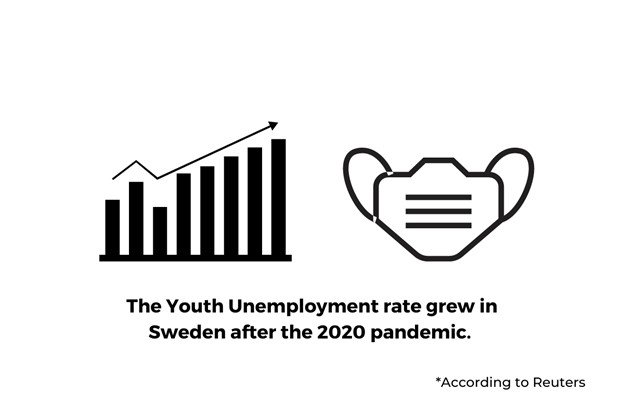
- As stated by Reuters, Sweden’s youth unemployment increased from 19.8% to 29.8% after the pandemic.
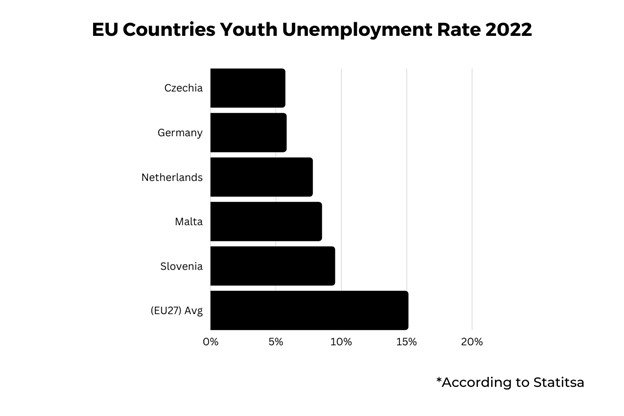
- As per the same Statista report mentioned above, Czechia had the lowest youth unemployment, at just 5.7%, in 2022.
- IZA World of Labor credited Germany’s low youth unemployment to its dual apprenticeship programs.
- According to the NextGenerationEU website, the European Union plans to invest €806.9 billion in the Next Generation EU initiative.
- According to Research Gate, academia should provide youth with the necessary skills demanded in the labor market.
Which European Union Member Countries Have the Highest Youth Unemployment Rate?
Statista is a company specializing in data, statistics and company insights. It is trusted by over 2500 companies, including Google and Facebook, for market insight. A recent report by Statista shows the youth unemployment rate in the European Union in 2022.
The piece covered countries with both relatively higher and lower unemployment rates. The report mainly concerns the youth of ages 15-24.
As a point of reference, the average unemployment rate across the EU27 countries was 15.1%.
Spain and Greece
According to the Youth Unemployment report, Spain’s unemployment rate was the highest among all EU countries at 32.3%. Following this, Greece’s unemployment rate in 2022 was 27.3%.
Italy
Italy had the third-highest unemployment rate of 23.9%.
Sweden and Romania
Sweden and Romania were among the top 5 countries with the highest unemployment rate, with Sweden at 23.4% and Romania at 22.8%.
Cyprus and Luxembourg
Following these, Cyprus had a youth unemployment rate of 21.7%, while Luxembourg stood at 19.5%.
Latvia and Slovakia
Further down the line, Latvia’s youth unemployment rate was 19.2%, and Slovakia’s was 18.8%.
France and Belgium
France’s rate was 18.2% and following it, Belgium had a rate of 17.7%, which gives these two countries a moderate unemployment rate.
Portugal and Croatia
Portugal had a rate of 17.6%, while Croatia had a rate of 17.4%. The difference between Portugal’s and Croatia’s unemployment was only 0.2%.
To paint a complete picture, let us look at non-European countries. In another report by Statista about the Youth unemployment rate of G20 countries, South Africa, a non-union member state, had an unemployment rate of 64.18% in 2021. South Africa had the highest unemployment rate among all G20 countries. Next on the list, Brazil’s unemployment rate was almost half of the formerly mentioned, at 31.9%, while Argentina had an unemployment rate of 29.89%.
Why is Youth Unemployment High in Spain?
Foundation for Economic Education (FEE) is a right-wing think tank based on spreading economic principles, especially that of a free market. FEE is a member of the State Policy Network (SPN), a non-profit organization aiding think tanks by connecting reliable foundations and offering resources to these leaders.
A piece published by FEE in 2022 titled “Why Spain Routinely Has One of the Highest Unemployment Rates in Europe” provided insight into why this phenomenon could have occurred. According to the article, high unemployment occurred due to regulations, or more specifically, the over-regulation of the labor market. The piece refers to The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and its published index, which showed restrictions on the non-English speaking markets, such as France, Italy and Spain. The regulations resided in the Employment Protection Legislation (EPL), which provided employee safety for hiring and firing workers.
The article further stated that these restrictions led to employers aiming for short-term contracts over long-term ones. A 2019 study by the IZA Institute of Labor Economics titled the Dual Market Revisited backs up this statement, known. The IZA Institute of Labor Economics is a research institute supported by the Deutsche Post Foundation. The study revealed that 90% of hires in Spain are based on temporary work contracts.
The aim is to avoid paying severance costs to long-term employees, which leads to the preference for these short-term contracts. Fixed-term or short contract contracts cause job insecurity and discouragement within the Spanish workforce. This occurrence is called the ‘Dual Labor Market System’.
The FEE article suggested another reason for the high unemployment in Spain. They pinpointed the increased social security tax on employers, being 29.9%. It indicated that this would lead to declining working hours and wages, resulting in a lack of incentive for workers to join the force.
Even though the article covered widespread unemployment, it would be safe to assume these factors contribute to youth unemployment in the country.
Why Is Sweden’s Youth Unemployment So High?
Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world, with over 2500 journalists. They published an article in 2020 analyzing Sweden’s youth unemployment and precisely covered its specifics.
The article explained Sweden’s regression towards worse youth unemployment after the pandemic. The unemployment rate went from 19.8% a year earlier to 28.9%.
A 2022 Statista report, Sweden’s Youth Unemployment, also reported a rising unemployment rate in the country since 2018. While there is no specific research on why this occurred, we can refer to an article by EconStor for why this happened.
EconStor is a publishing platform for Economic research and literature, with over 212,000 papers. They published a report on European youth unemployment, which could offer insight into suggested reasons for this occurrence in Sweden. It is, however, worth noting that the article is relatively old, dating back to 2013. It provided reasons such as:
- Lack of job-specific experience of the youth
- High severance pay leads to hiring hesitance by employers
- Shorter credit history
- Recessions
Which European Union Member Countries Have the Lowest Youth Unemployment Rate?
The Statista report on youth unemployment in 2022 also presented countries with the lowest unemployment rates.
Czechia
The country with the lowest unemployment rate was Czechia, with a youth unemployment rate of only 5.7%.
Germany
Germany followed Czechia closely, with a youth unemployment rate of only 5.8%. Germany’s general population, however, has a low youth proportion.
IamExpat is a leading English media platform for Germany, Netherlands and Switzerland. It holds fairs, workshops and webinars. In a 2021 article by the organization, the proportion of young people to the general population was exhibited. It stated that out of 83.2 million people in Germany in 2020, only 8.4 million belonged to the youth, specifically ages 15-24.
Netherlands, Malta and Slovenia
Other Scandinavian countries also follow the low unemployment rate trend, with the Netherlands at 7.8%, Malta at 8.1%, and Slovenia at 9.5%.
Hungary and Austria
Hungary and Austria also had low unemployment rates compared to many other EU members. Hungary had a 9.5%, and Austria had a 10.3% youth unemployment rate.
Bulgaria and Poland
Bulgaria’s rate was a minuscule 10.6%, and Poland’s was 11.3%. This is much less significant when considering Spain’s staggering rate of 32.3%.
Ireland, Finland and Lithuania
Moreover, Ireland’s youth unemployment rate was 12%, Finland’s 12.1% and Lithuania’s 12.4%.
Denmark and Estonia
Denmark’s youth unemployment rate was 13.6%, while Estonia’s was 14.8%, still on the lower end of many EU countries positions.
Why Is Germany’s Youth Unemployment So Low?
The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is Germany’s cabinet-level ministry. Their publications include The German Vocational Training, which described the dual apprentice system as providing young people with training for nationally recognized positions. This training contains cooperation between vocational centers and small to medium-sized businesses.
Companies benefit through this system by avoiding recruitment costs and having market-centered, skillfully trained employees.
It is worth noting that countries with lower unemployment rates, such as Austria, Switzerland, Luxembourg and Denmark, have also applied this system.
The IZA World of Labor is an online platform centered around analyzing policies based on evidence. It deals with labor market matters and has the World Bank as one of its institutional partners.
IZA’s article on Germany’s youth unemployment trends from 2000-2018 validated the dual apprenticeship program. According to the report, Germany’s low unemployment directly resulted from its dual apprenticeship system.
It argued that the system led youth to learn in-demand skills and equip them with the necessary qualifications.
Furthermore, it stated that this method smoothened the transition from school to work and lowered barriers.
Moreover, the apprenticeship period is three years and is a better alternative for employers as they could get a feel for the workers and their productivity. However, Germany is still strict with its employment laws. Thus, workers cannot be fired sporadically and hired for short periods to test productivity. However, the growing importance of academic education over vocational training may threaten Germany’s dual apprenticeship system.
Youth Employment Opportunities in the EU in 2022
The European Student Think Tank (EST), an international NGO, aims to involve young Europeans in policy-making discussions. It has ambassadors in over 35 countries and enables research on vast topics such as the environment, security, etc. Their article on European initiatives for youth in 2022 provides insights into EU countries’ efforts on this front.
The European Year of Youth
As claimed by the article, during the pandemic, the European Union launched an initiative known as the European Year of Youth to compensate for the sacrifices made by the youth during the period. The aim was to develop policies for the youth through conferences and activities.
The Youth Guarantee
The Youth Guarantee, initially established in 2013, provided jobs, apprenticeships, education, and training for 24 million people, as long as the individuals in question were under 30. The Reinforced Youth Guarantee was established after the pandemic. The updated scheme aims to aid disadvantaged individuals with an effort to be inclusive. The new plan now offers personalized counselling.
Vocational Education and Training
The European Union Commission gave further insight into the new branch of this scheme in its youth employment support report. It touched on Vocational Education and Training (VET), which would encourage skill learning in innovative and modern ways, and debriefed apprenticeship policies. They plan to create incentives for employers, especially small to medium-sized businesses, for apprenticeship cooperation and involvement.
Next Generation EU
NextGerationEU is a post-pandemic temporary economic recovery plan by the EU. The European Union commission has planned to invest €806.9 billion in this initiative, alongside others for the next generation.
Referring to the initial article by the EST mentioned above, other plans were also set for helping the youth. This includes Slovenia’s plan to offer monetary incentives for 18 months for hiring people up to 25. They also planned to offer open-ended contracts, mentoring opportunities, and digital training for a minimum of 30 hours per week.
European Social Fund Plus
Additional plans were set, such as the European Social Fund Plus (ESF+), established by the European Commission, which developed plans for member states. According to this, EU countries with high rates of unemployed workers with completed education would dedicate a minimum of 12.5% of the ESP+ funding for the youth.
Factors Contributing to Youth Employment in European Union Countries
Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union, published an article titled Youth unemployment in 2022. It deals with the difficulty of transitioning from school to the labor force in the EU countries. According to the piece, the global pandemic had a massive impact on the EU labor market, especially on youth.
Research Gate is a research networking web platform with features in popular media platforms such as The New York Times. It published a report on EU youth unemployment in 2022 and offered insight into the subject. According to the piece, youth unemployment amplified following the recent economic depression. It listed the following reasons for this:
- The transition from the education system to the labor market.
- The financial support offered to young people by their families.
- Increasing importance attached to more extended periods of education.
- Economic policies and distribution of opportunities in society.
- Lack of education and training apprenticeships.
- Insufficient experience.
- Lack of signals that could show employers a candidate’s productivity.
- Employment protection.
The debate on the causes of youth unemployment within the research community is prevalent. Their findings can aid in drawing a picture of the possible reasons.
The article further dwells on the need for equipping the youth with tools to transition into the labor force with ease, as research finds a massive reason lies in the gap between the market demand and the skills supplied by the education system. It stated that the government needs to provide more efficient grants, thus impacting youth unemployment.
Conclusion
Countries with the highest unemployment rate had their conditions exacerbated by the 2020 pandemic, which affected the economy and the labor market. Sweden went through a drastic unemployment rate increase due to the pandemic. While some countries suffered from the pandemic, others’ policies and laws affected their labor market. Spain, for example, negatively affected employers’ decisions due to its strict employment laws and high social security tax.
Countries with the lowest unemployment rates benefited from initiatives and policies directly linked to equipping their youth with skills corresponding with the market’s demand. Germany pulled itself out of a low unemployment rate and set an example of practical plans that could be implemented. It prioritized its youth’s needs and developed an efficient system.
European Countries’ members took many initiatives to combat the disadvantages their youth faced through systemized Youth Guarantee plans. It aimed to aid its youth through investments, programs, and projects. The impact can be seen through the 24 million people supported by the Youth Guarantee Program.
As we can tell, some EU member countries have high levels of unemployment. The countries experience this phenomenon due to various ineffective economic policies or laws, leading to higher barriers in the job market. The policies lead to insecurities within employers when hiring labor, especially youth labor, resulting in unemployment rates. However, some countries tackled youth unemployment rates through policy-making and initiatives.








![How to Improve Interpersonal Skills? [6 Steps] 13 How to Improve Interpersonal Skills](https://zoets.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/pexels-fauxels-3184357-scaled-e1708708387711.jpg)
![How to Improve Employee Welfare? [7 Ways] 14 How to Improve Employee Welfare](https://zoets.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/pexels-alexander-suhorucov-6457577-scaled-e1708707251724.jpg)


